...to Geog 111 Main Page and Course Description
...to Geog 111 Syllabus
...to Geog 111 Course Schedule and Lecture Outlines
...to Geog 111 Course Project
Course Conclusions
Two General Course Goals:
1. To instill an appreciation of natural characteristics of the environment, and in particular, Earth's landforms, through an understanding the natural processes that shape these landforms
An introduction to the geographic contributions to environmental
science: traditional fields such as geology, biology, botany, meteorology
with a focus on the natural environment
2. To introduce you to some major environmental issues and concerns: in essence,
issues that arise out of the intersection of the natural environment and human
activities in that environment.
An introduction to environmental studies: involves basic understanding
of natural processes, but broader: pull together elements from the diverse
environmental sciences and add a focus on human relationships to and activities
in the environment
Geography has always been a mixture of environmental science (physical
geography) and environmental studies (environmental geography)
Introduction to Earth's Physical Environment

1. Defining Geography
2. Introduction to Earth's Physical Environment
3. Classifying the Natural World
4. Natural Cycles
5. Time and Space and Environmental Change
Introduction to Human Environmental Relations

1. Human Environmental Relations: Introduction
2. Human Environmental Relations: Examples
3. Human Perspectives on the Physical Environment
4. Human Forces Behind Environmental Issues
5. Human Induced Imbalances
6. Interest in Environmental Issues
7. Sustainable Development
Portraying the Earth

1. The Nature of Maps
2. Developments in Mapping: Computer aided Mapping
Introduction to the Atmosphere
1. Composition of the Atmosphere
2. Vertical Structure of the Atmosphere
3. Weather and Climate
4. Elements of Weather and Climate
Introduction to the Hydrosphere
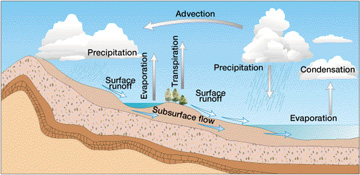
1. The Nature of Water
2. The Hydrologic Cycle
The Process of Studying Landforms
Internal Processes: building up landforms
External Processes: breaking down landforms: forces in atmosphere + hydrosphere
Weathering, Mass Wasting, and Erosion
Denudation: disintegration, wearing away, and removal of rock material; implies a lowering of earth's surface
1. Weathering: processes that break up rock at the earth's surface
1a. A Typology of Cracks and Crevices in Rock:
1b. Weathering Agents
2. Mass Wasting: processes that move fragmented rock short distances down slope
3. Erosion
Fluvial Processes: any environmental processes involving the flow and movement of water
on the Earth's surface
1. Impact of Fluvial Processes on the Landscape
1a. Traditional Theory of Landform Development: The Geomorphic Cycle
1b. Critique of Davisian Theory: Crustal Change and Slope Development
1c. Equilibrium Theory
2. Fundamental Definitions and Concepts of Fluvial Processes
3. Stream Channels: Key Characteristics of individual streams and rivers
4. Stream Systems: how streams and rivers relate to each other
5. Shaping and Reshaping of Valleys by Fluvial Processes
Karst and Hydrothermal Processes: Underground Water and Landforms
1. Karst Processes and Landscapes
Related to chemical weathering: breakdown and removal of rock due to chemical reaction between water and rock
Relatively widespread effect on earth's surface
1a. Solution and Precipitation
1b. Caverns and Related Features
1c. Karst Topography
2. Hydrothermal Features
In essence: underground water heated by magma then forced to earth's surface
2a. Hot Springs
2b. Geysers
2c. Fumaroles
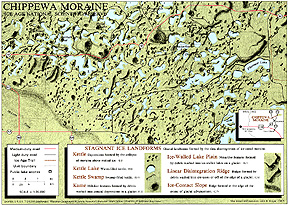
Glaciers and Glacial Landforms
The role of ice, and in particular moving ice - glaciers - in shaping landforms
What we can see today in the landscape is the result of existing glaciers and the most recent ice age: the Pleistocene
1. Glaciers Formation and Flow
Overall result of glacial flow is a form of erosion by water
2. Mountain Glaciers (skip this section)
3. Continental Ice Sheets and Glaciers
3a. Development and Flow of Pleistocene Glaciers
3b. Erosion by Ice Sheets
...Transportation by glaciers...
3c. Deposition by Ice Sheets and Glaciers during Pleistocene
Broadest Goals of Course:
Appreciation that our environment is dynamic and constantly being modified by natural processes and human activities.
Basic understanding of the natural processes
Basic understanding of human induced changes in the environment, why they occur, their impact, and complexity
Heightened awareness of the complexity and importance of the environment we live in and depend upon in so many ways. Basis for a lifelong appreciation for, and concern about, the Earth's environment.
E-mail: jbkrygie@owu.edu
...to Geog 111 Main Page and Course Description
...to krygier teaching page.
...to krygier top page.