Geography 353 Cartography and Visualization
...to Geog 353 Main Page and Course Description
...to Geog 353 Syllabus
...to Geog 353 Course Schedule and Lecture Outlines
...to Geog 353 Laboratory Information and Student Projects
Geog 353 Lecture Outline: Geographic Framework
Update: 17/8/19
Making Maps book: Chapter 5: Geographic Framework
- much of the information on this page was condensed, consistently
illustrated, and made much better for the 5th chapter in Making Maps.
- use this page for additional reference.
Introduction
Geographic Framework
- I. Flatten the earth's curved surface: Map Projection
- II. Zoom in: Map Scale
- III. Locate: Map Coordinates
I. Introduction to Map Projections and Map Design

- Map Projection: peel and flatten the earth...like
an orange peel
Map projections are an important aspect of all mapping as all maps require the
transformation of the surface of the spherical earth to a flat surface
This transformation always introduces some kind of distortion
- distortion of area, shape, angles, etc.
We are used to seeing the world distorted: it looks natural
The goal is to select a map projection whose distortion does not interfere with
the purpose of any given map.
- infinite number of map projections
- selection of appropriate base map projection driven by map content
Projections are important to mapping and GIS:
- use them to focus reader's attention
- amplify and provide selective detail for map's message
- most important: poorly chosen map projections can distort your thematic data
Vital Map Projection Issues:
- What are the basic characteristics of the map projection process?
- What are the basic kinds of map projections and distortions?
- Choosing Appropriate Map Projections
Cool Free Map Projection Software (Download):
G.Projector
2. What are the basic characteristics of the map projection process?
- how does map projection work?
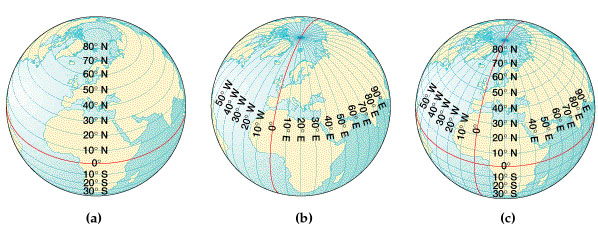
The geographic grid or graticule
- Locations on the sphere: latitude and longitude (one of many coordinate systems)
But globes are not that useful for most mapping tasks...so flatten the earth:
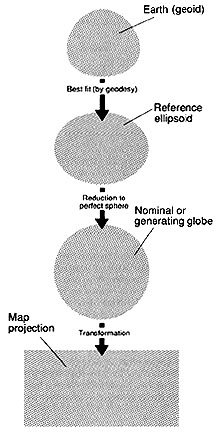
- earth: geoid
- reference ellipsoid: geodesy
- called nominal, reference, or generating globe
Map projection: transformation of the spherical surface into a plane surface
- All meridians and parallels are transformed in this process: the graticule
- All human and physical earth features (coasts, rivers, lakes, boundaries, etc.)
are also transformed in this process
3. What are the basic kinds of map projections and distortions?
Mark Monmonier in How to Lie with Maps: map projection is a "white lie"
Map projection process always results in some kind of distortion
- distortions of areas, shapes, distances, and directions
- something must always give: cannot preserve all of these together
- Making Maps PDF) Ch 5. Distorting Data
- Important: projections matter because of what they do to mapped data
Tissot's Indidicatrix: perfect circles of equal size on the globe; reveal
patterns of distortion on projected maps.
Example: Mercator Projection: Distortion of areas but not shapes...
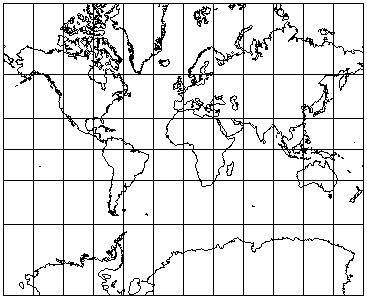
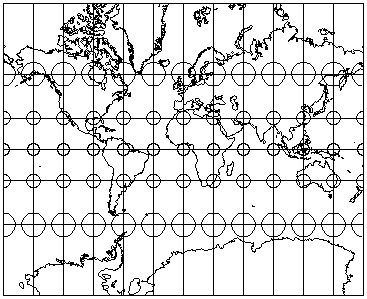
Example: Equal Area Rectangular Projection: Distortion of shapes but not areas...
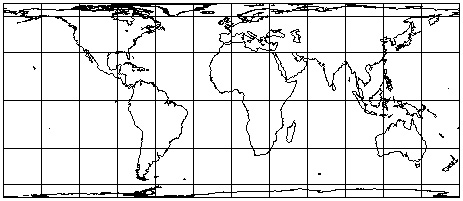
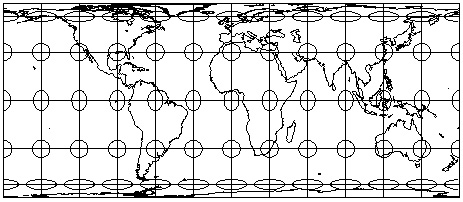
Importance of scale and map projection
- large scale mapping: distortion less noticeable; important if digital (GIS)
- small scale mapping: fundamentally important
Next:
- three basic kinds (categories, families) of map projections
- five major kinds (categories) of map projections
3a Three Basic Kinds (Families) of Map Projections
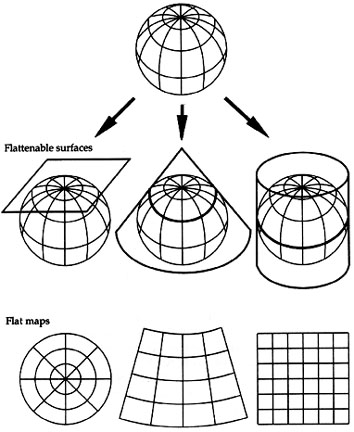
Based on the idea of developable surfaces: attribute of the map projection
process: what kind of flattenable surface are you projecting the sphere onto?
- light source of the projection inside globe
- shadow cast on plane, cylinder, cone
- corresponds to azimuthal, cylindrical, and conic projection families
- gives you very different looking maps with different distortions
- Tangent and Secant Cases with distortions (dark = more distortion)
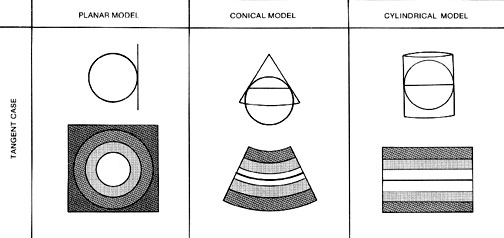
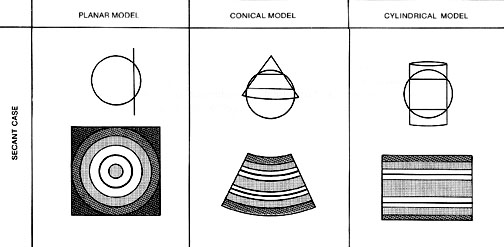
Azimuthal Family:
Projection onto a plane
- tangent at a point on the sphere (simple form): standard point
- or pass through the sphere (secant form): standard line
Tangency can be varied: varies the projection
- polar aspect: tangency at a pole
- oblique aspect: tangency at mid-latitude
- equatorial aspect: tangency at equator
Distortions increase from standard point or line
- increase outward in concentric bands
- conformal azimuthal projections: area exaggeration increases outward
- equal area azimuthal projections: shape distortion increases outward
- can be varied to preserve area, angle, distance, or direction
Cylindrical Family:
Conic Family:
Second major aspect of map projections
- Review five major kinds (categories) of map projections based on the
characteristics they preserve from the spherical earth (what they
don't distort)
3b. Map Projections and what they Preserve from the Spherical Earth
Preserving Area: Equal Area or Equivalent Projections
- area relationships are preserved
- linear or distance distortion occurs as a consequence, skewing shape
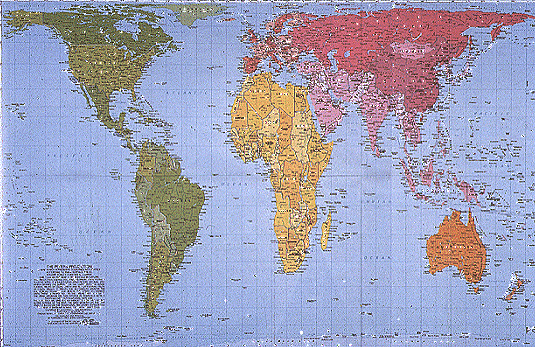
- Peters Equal-Area Map Projection: you give up shape to preserve area
Equal area projections very important to thematic mapping as much of thematic
mapping consists of mapping area data
Equal area projections are a good general default for all thematic maps:
- Lab Project!
- US States: conic equal area projections are optimal
Map Projections in ArcGIS
1) Start ArcMap
2) Add, to your data frame a base map Countries.lyr (in ESRIDATA_2000/world folders)
- make sure the layer is visible.
3) Add a lat/long graticule as another layer
- from the ESRIDATA_2000/world folders add latlong.shp
Remember: equal area (equivalent) is best default: so change projection
4) Right mouse click on the data frame your layers are in, and select Properties.
- select the Coordinate System tab.
- select Predefined then Projected Coordinate Systems
- ArcGIS gives you some categories to choose from: we have a world map, so
select the World folder to see a few dozen map projections appropriate
for world maps.
- select the Robinson and hit ok
5) Check out the characteristics of the Robinson in ArcGIS's desktop help.
- It preserves neither shape or area! But it looks ok.
While the equal area map projections are the best default
- several other options for special cases
Preserving Shape: Conformal Projections

- Mercator map projection is conformal (and cylindrical)
- Angular relationships are preserved from points, and shape is preserved for
small areas around a given point
- Can never preserve areas (Equal Area) and shape (Conformality) at the same time
- Useful for navigation, and mapping phenomena with circular radiation patterns
Preserving Distance: Equidistance Projections
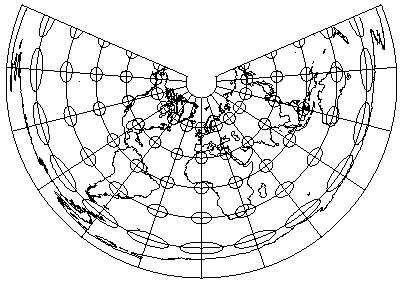
- Equidistance map projection is equidistant (and conic)
- Distance is correct from one to all other points, or from a few points to
others, but not from all points to all other points
- Cannot preserve distances (Equidistance) and preserve area (Equal Area)
Preserving Direction: Azimuthal Projections
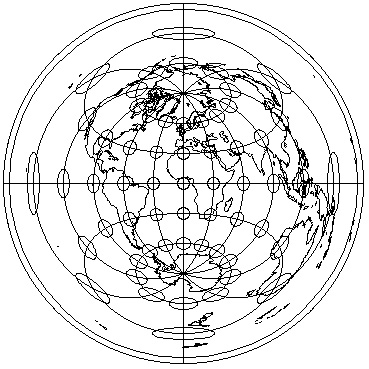
- Azimuthal map projection preserves direction (and is azimuthal)
- Preservation of direction from one central point to all other points
- Can occur on equal area, conformal, and equidistant projections
Compromise Projections
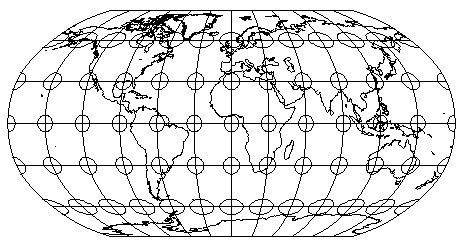
- Robinson map projection: preserves nothing, but looks good (and is cylindrical)
- a compromise which attempts to preserve enough of area, shape, distance, and
direction so that the earth "looks right"
- was used by National Geographic on their World Maps
4. Choosing Appropriate Map Projections
- Basic guidelines and projections appropriate for particular circumstances
- Given the purpose and goal of your map, consider...
Projection properties:
- Which projection family: azimuthal, cylindrical, conic?
- often more of an aesthetic choice
- Which properties need to be preserved given the purpose of the map?
- vital! not aesthetic!
- equivalency (areas)
- conformality (shape)
- equidistance (distance)
- azimuthality (direction)
- ArcMap:
- Help: Map Projections
- or projection name: Mercator, Albers...etc.
Map Projection Center:
- center the projection given the purpose of the map?
- Key: when setting up a base map: select a standard point or line near the
center of your area of interest to minimize distortion
- Recentering map projections: center the map projection on the area of interest
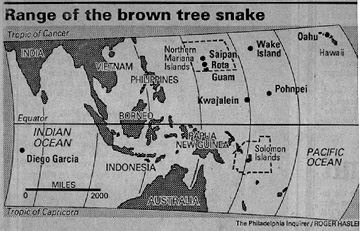
- Poor centering of map projection: cut out of a world map projection centered...?
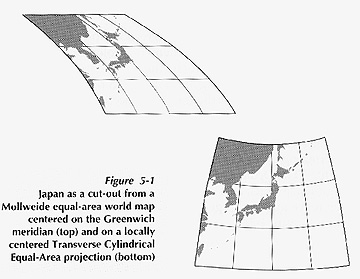
- Poor and Good centering of map projection: recenter to focus on area of interest
- Recentering in ArcMap:
- 1) return to the properties of your dataframe and the Coordinate System tab
- 2) the Robinson projection you chose should be hi-lighted in the window: hit the Modify button
- in the Central_Meridian row type -84 (84 degrees W. of Greenwich, 0 degrees)
then OK
- 3) The world should recenter on the meridian running through Delaware Ohio.
- try this with a map of the US
- Your Project: you will adjust the center of the projection so that your state/s does
not look tipped
Familiarity and Aesthetics
- Will the projection be familiar enough to users so as not to detract from the
purpose of the map?
- is it appropriate to "surprise" the user with an unfamiliar projection to
communicate something?
Suggestions for Mapping the World
- equivalency (areas preserved) is fundamentally important
- ArcGIS) Mollweide
- ArcGIS) Robinson
- ArcGIS) Peters (nope!)
Suggestions for Mapping Continents and Large Countries
Projections suitable for world maps are usually not suitable for mapping continents.
- ArcGIS) Lambert equal area azimuthal projection
...and for the United States...
- ArcGIS) Albers equal area
- Lab: this is best!
Suggestions for Creative Solutions to the Employment of Projections
1. Using interrupted map projections
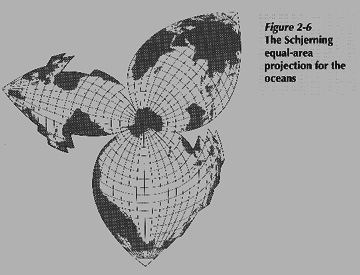
- Schjerning map projection: interrupted
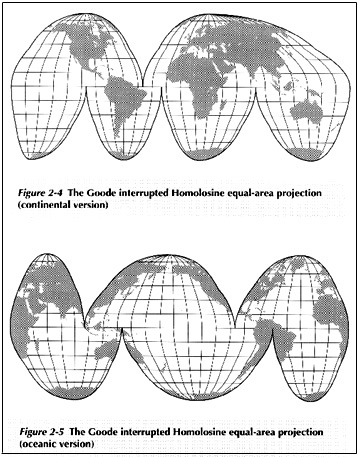
- Goodes map projection: interrupted over oceans (top) versus land (bottom)

- Fuller map projection: cut and assemble globe
2. Using hemispheric map projections: the view from space
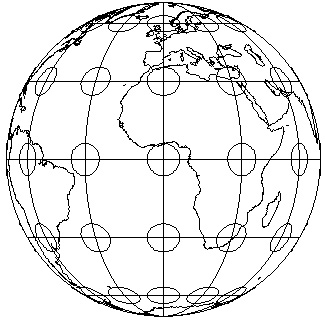
- Orthographic map projection: like lookin' at a globe

- Orthographic map projection: used for locator insets
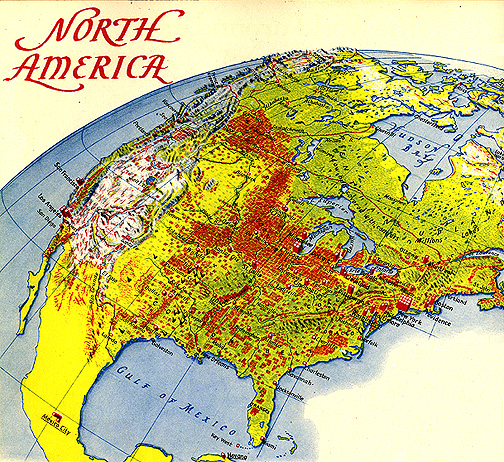
- Erwin Raisz oblique map projection: just cool
3. Enlarging the center of the map
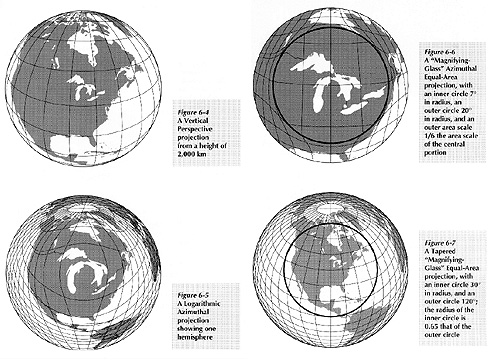
- Various odd map projections: focus attention on area of interest
4. Showing rings of activity
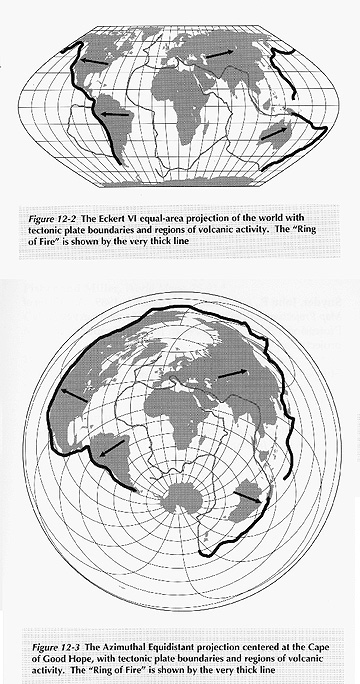
- The "Ring of Fire": Eckert versus Azimuthal Equidistant map projections
In all these cases you have to understand what is being distorted
- Don't select a projection on its "look" alone

- The UPS Map Projection: something wrong?

- For Football Fans: about as amusing as map projections get
"The map projection provides the geometrical framework for all the points,
lines, and areas compiled on the final map. Projection is a key element in the
overall design. It controls the locational accuracy and final appearance of the
mapped area and can be used to provide a focus for the map's message." (Borden Dent)
II. Map Scale
- Making Maps PDF) Ch 5. Map Scale
III. Map Coordinates
- Making Maps PDF) Ch 5. Map Coordinates
Conclusions
Lab project: setting up your state map in ArcGIS/ArcMap
- You will have to choose the map projection of your state map
E-mail: jbkrygier@owu.edu
...to Geog 353 Main Page and Course Description
...to krygier teaching page.
...to krygier top page.
OWU Home
OWU Geology and Geography Home